Oxygen has 6 valence electrons. Valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost shell of an atom.
Oxygen, a chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8, is an essential component of the Earth’s atmosphere. It is also a key element in various biological and chemical processes. Understanding the number of valence electrons in an oxygen atom is crucial in comprehending its reactivity and its ability to form chemical bonds.
In this blog, we will explore the significance of valence electrons, their role in oxygen’s chemical behavior, and the impact of oxygen’s electron configuration on its interactions with other elements. By the end of this discussion, you will have a clearer understanding of the importance of valence electrons in oxygen and its implications in various scientific and practical applications.
The Basics Of Valence Electrons
Oxygen has six valence electrons in its outer shell, making it a key player in chemical bonding. Understanding the basics of valence electrons helps to explain oxygen’s reactivity and its role in forming various compounds.
What Are Valence Electrons?
Valence electrons are electrons in the outermost shell of an atom.
They determine the chemical properties of an element.
The Role Of Valence Electrons In Chemical Bonding
Valence electrons participate in bonding with other atoms.
They form ionic and covalent bonds in molecules.
These bonds are crucial for creating compounds.
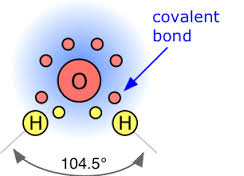
Credit: socratic.org
Peering Into The Atomic Structure
Oxygen possesses six valence electrons in its atomic structure, crucial for chemical bonding. Understanding the electron configuration sheds light on oxygen’s reactivity and its role in forming diverse compounds. The valence electrons influence oxygen’s behavior in reactions and its significance in sustaining life processes.
The Atomic Model
The study of atoms and their structure has fascinated scientists for centuries. To understand how many valence electrons oxygen has, we need to delve into the atomic model. Atoms are the building blocks of matter, and they consist of three main components: protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons carry a positive charge, neutrons have no charge, and electrons are negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus of the atom.
Electron Shells And Energy Levels
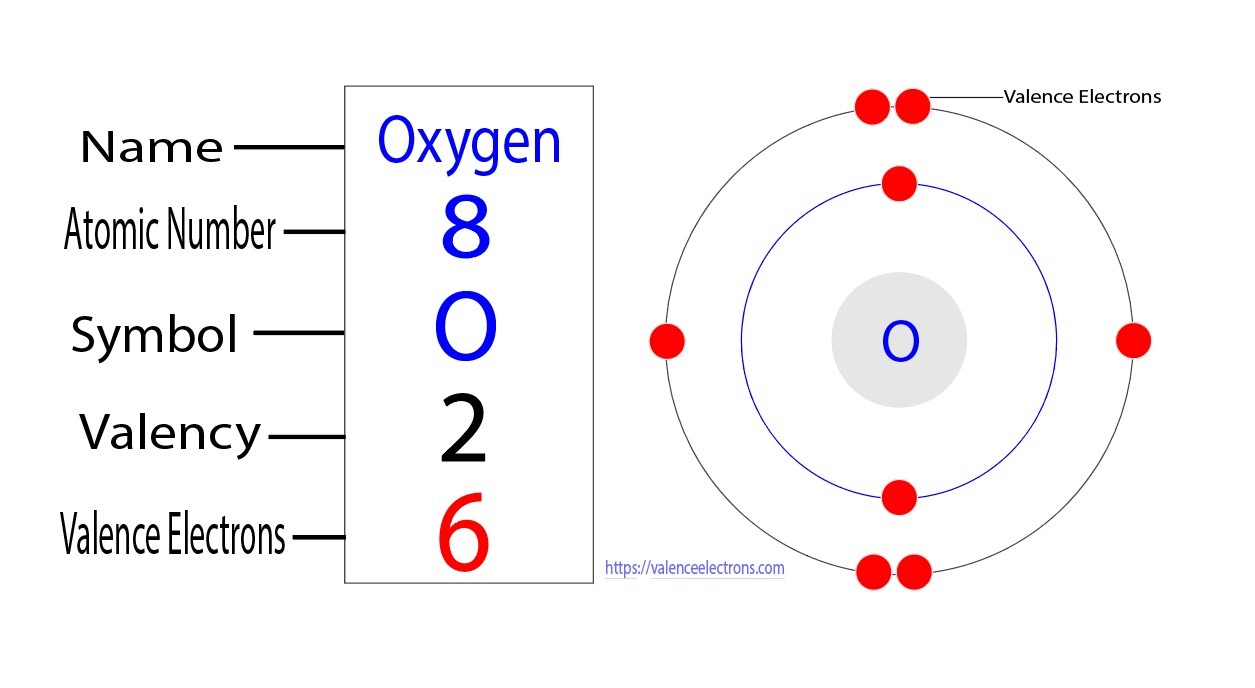
Within an atom, electrons are organized into shells or energy levels. These energy levels are arranged at increasing distances from the nucleus. How Many Valence Electrons Does Oxygen Have? The first energy level can hold a maximum of 2 electrons, while the second level can hold up to 8 electrons. The third energy level can hold a maximum of 18 electrons, and so on. Oxygen, with an atomic number of 8, has 8 electrons.
Therefore, its electron configuration is 2-6. This means that oxygen has 2 electrons in its first energy level and 6 electrons in its second energy level. Peering into the atomic structure of oxygen reveals a fascinating arrangement of electrons. The two electrons in the first energy level are closest to the nucleus, while the remaining six electrons are in the second energy level.
These six electrons in the outermost energy level, also known as the valence electrons, play a crucial role in determining the chemical behavior of oxygen. Understanding the number and arrangement of valence electrons is essential in predicting how elements will react with one another. For oxygen, having six valence electrons means it is only two electrons away from achieving a stable configuration of eight electrons in its outermost energy level.
In conclusion, oxygen has 8 electrons, with 2 in the first energy level and 6 in the second energy level. Peering into the atomic structure and understanding the arrangement of valence electrons provides insights into the chemical behavior of oxygen and its interactions with other elements.
Oxygen’s Position In The Periodic Table
Oxygen is an element that is vital for life on earth, making up around 21% of the atmosphere. It is also a member of the periodic table, which is a chart that lists all the known elements in order of their atomic number. Oxygen’s atomic number is 8, which means it has 8 protons in its nucleus, and it is located in Group 16, also known as the chalcogens, and Period 2 of the periodic table.
Understanding Periodic Trends
The periodic table is arranged in such a way that elements with similar properties are placed in the same group, while those with different properties are placed in different groups. The elements in each group have the same number of valence electrons, which are the electrons in the outermost shell of an atom that are involved in chemical reactions. Understanding periodic trends helps to predict the chemical behavior of an element based on its position in the periodic table.
Group And Period Insights
Oxygen’s position in Group 16 means that it has 6 valence electrons, which is the number of electrons needed to fill its outermost shell. This makes it highly reactive, and it readily combines with other elements to form compounds. Oxygen also has a high electronegativity, which means it has a strong attraction for electrons and can form polar bonds with other elements. In Period 2, oxygen is located between fluorine and nitrogen, and it shares some properties with both of these elements.
| Element | Atomic Number | Valence Electrons |
|---|---|---|
| Fluorine | 9 | 7 |
| Oxygen | 8 | 6 |
| Nitrogen | 7 | 5 |
- Oxygen is more electronegative than nitrogen, which means it has a stronger attraction for electrons.
- Oxygen is less electronegative than fluorine, which means it has a weaker attraction for electrons.
- Oxygen has a smaller atomic radius than both nitrogen and fluorine, which means it is more likely to form covalent bonds.
Overall, understanding the position of oxygen in the periodic table can help us predict its chemical behavior and its interactions with other elements.

Credit: www.youtube.com
Diving Into Oxygen’s Electron Configuration
Oxygen’s electron configuration reveals that it has 6 valence electrons. These outer shell electrons play a crucial role in chemical reactions and bonding, making oxygen a key element in various compounds and biological processes. Discovering the number of valence electrons in oxygen sheds light on its reactivity and its significance in our everyday lives.
Electron Configuration Explained
Electron configuration is a fundamental concept in chemistry that describes how electrons are arranged within an atom. It provides valuable insights into an element’s chemical behavior and its ability to form bonds with other elements. Understanding the electron configuration of oxygen is crucial in comprehending its unique properties and reactivity. Let’s dive into oxygen’s electron configuration to unravel its mysteries!
Oxygen’s Specific Electron Arrangement
Oxygen, with its atomic number of 8, has 8 electrons in total. These electrons are distributed among different energy levels or shells, namely K, L, and M. The electron configuration of oxygen can be represented as 1s2 2s2 2p4.
In simpler terms, oxygen has two electrons in its first energy level (K shell), two electrons in its second energy level (L shell), and four electrons in its third energy level (M shell). The first energy level can hold a maximum of 2 electrons, while the second and third energy levels can accommodate up to 8 electrons each.
The 2s orbital in the second energy level contains two electrons, while the 2p orbital, also in the second energy level, contains the remaining four electrons. The 2p orbital has three suborbitals, each capable of holding a maximum of 2 electrons.
It is important to note that the electron configuration of oxygen determines its chemical behavior. The presence of 6 valence electrons in the outermost energy level (2s2 2p4) makes oxygen highly reactive and prone to forming covalent bonds with other elements. These valence electrons are responsible for oxygen’s ability to participate in chemical reactions and play a vital role in the formation of compounds like water (H2O) and carbon dioxide (CO2).
Understanding the electron configuration of oxygen helps us appreciate its significance in various chemical reactions and its role in sustaining life on Earth. Whether it’s the process of respiration or the intricate mechanisms of photosynthesis, oxygen’s electron arrangement plays a crucial role in supporting life as we know it.
In conclusion, oxygen’s electron configuration, specifically the arrangement of its 8 electrons in the K, L, and M energy levels, is a fundamental aspect of its chemical behavior. By exploring and comprehending this electron arrangement, we gain a deeper understanding of oxygen’s unique properties and its essential role in various chemical processes.
Valence Electrons Of Oxygen Revealed
Oxygen has 6 valence electrons. These electrons are crucial for forming chemical bonds and are the reason behind oxygen’s reactivity and ability to combine with other elements. Understanding the valence electrons of oxygen is essential in comprehending its role in various chemical reactions.
Counting The Electrons
Oxygen, a key element in the periodic table, has six valence electrons. Understanding the concept of valence electrons is crucial in comprehending the chemical properties and reactivity of oxygen.
Why Oxygen Has Six Valence Electrons
Oxygen has a total of eight electrons, with two located in the innermost shell and six in the outer shell. These outermost electrons are known as valence electrons, and they determine the element’s ability to form chemical bonds. In the case of oxygen, it has six valence electrons as it belongs to group 16 of the periodic table.
The Significance Of Oxygen’s Valence Electrons
Oxygen, as an element, has six valence electrons. These electrons play a significant role in chemical reactions, determining the element’s reactivity and its ability to form bonds with other elements. Understanding the number of valence electrons in oxygen is crucial in studying its behavior in various chemical processes.
Chemical Reactivity And Bonding
Oxygen, with its six valence electrons, plays a crucial role in determining the chemical reactivity and bonding properties of this element. Valence electrons are the electrons located in the outermost shell of an atom. They are responsible for the formation of chemical bonds, which are essential for the stability and structure of molecules.
Due to its electron configuration, oxygen is highly reactive and readily participates in chemical reactions. It has a strong tendency to gain two electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration, known as the octet rule. This reactivity makes oxygen a key component in various chemical processes, including combustion, respiration, and oxidation reactions.
Oxygen’s valence electrons are particularly important in the formation of covalent bonds. Covalent bonds occur when atoms share electrons, resulting in the formation of molecules. Oxygen commonly forms covalent bonds with other elements, such as hydrogen, carbon, and nitrogen, to create a wide range of organic and inorganic compounds.
Oxygen In Organic And Inorganic Compounds
Oxygen’s valence electrons are found in a variety of organic and inorganic compounds, playing a crucial role in their properties and functions.
In organic compounds, oxygen often appears as part of functional groups, such as hydroxyl (-OH), carbonyl (C=O), and carboxyl (-COOH) groups. These groups contribute to the characteristic properties of organic compounds, such as alcohols, aldehydes, ketones, and carboxylic acids. Oxygen’s ability to form multiple bonds and interact with other atoms allows for the diverse range of organic compounds found in nature.
In inorganic compounds, oxygen is commonly found in oxides, which are compounds formed by the combination of oxygen with other elements. Oxides play a vital role in various industries, including metallurgy, ceramics, and electronics. For example, iron oxide (Fe2O3) is responsible for the red color of rust, while silicon dioxide (SiO2) is the main component of quartz and glass.
In summary, the valence electrons of oxygen are significant in determining its chemical reactivity and bonding properties. Oxygen’s ability to form covalent bonds and participate in various chemical reactions makes it essential for the existence of life and the functioning of many industries.
Comparing Oxygen With Other Elements
Valence Electron Variations
Oxygen has 6 valence electrons.
Valence electrons determine chemical properties.
Periodic Table Neighbors Of Oxygen
Oxygen is in Group 16 of the Periodic Table.
Neighbors: Carbon, Nitrogen, Fluorine, and Sulfur.
Credit: praxilabs.com
Applications And Implications
Oxygen has six valence electrons, located in the 2p orbital of its outermost energy level. This configuration gives oxygen the ability to form two covalent bonds, making it a highly reactive element with many important applications and implications in chemistry and biology.
Oxygen In Everyday Life
Oxygen’s role in respiration is vital for human survival.
It supports combustion and sustains life in diverse ecosystems.
- Used in medical settings for respiratory therapies.
- Essential for water purification processes.
Advanced Applications In Science And Technology
Oxygen plays a key role in various scientific and technological advancements.
It is crucial in aerospace industries for propulsion and life support systems.
| Industry | Application |
|---|---|
| Healthcare | Used in oxygen therapy for patients. |
| Environmental | Facilitates wastewater treatment processes. |
| Energy | Utilized in oxy-fuel combustion for power generation. |
Frequently Asked Questions
How Many Valence Electrons Does Oxygen Have?
Oxygen has 6 valence electrons.
What Is The Significance Of Oxygen’s Valence Electrons?
Oxygen’s valence electrons determine its ability to form chemical bonds with other elements.
How Do Valence Electrons Affect Oxygen’s Reactivity?
The 6 valence electrons in oxygen’s outer shell make it highly reactive and able to form numerous compounds.
Why Are Valence Electrons Important In Chemistry?
Valence electrons determine the chemical properties and reactivity of an element, making them crucial in chemical reactions.
Conclusion
Understanding the number of valence electrons in oxygen is crucial for grasping its chemical behavior. With six valence electrons, oxygen forms stable compounds and participates in various reactions. This knowledge is essential for students and professionals in chemistry and related fields.
Stay curious and keep exploring!