Foxes, dogs, cats, birds of prey, and stoats are some animals that eat rabbits. Rabbits eat grass and plants, designed for high-fiber food.
Their predators affect their behavior and diet. Rabbits are also prey for raccoons, which hunt small mammals and steal bird eggs. Good quality hay and grass should be the majority of a rabbit’s diet. Beagles are popular rabbit-hunting dogs, as they can navigate through brush and force rabbits out to be chased.
Predators like red foxes, kit foxes, and gray foxes frequently prey on rabbits. This interplay between predator and prey shapes the ecosystem and behaviors of these animals.
Rabbit Predation: An Introduction
Rabbits play a crucial role in the food chain as both prey and herbivores. Understanding the predators of rabbits sheds light on the delicate balance of nature.
The Role Of Rabbits In The Food Chain
Rabbits are essential prey animals, serving as a vital food source for a variety of predators. They contribute to the ecosystem’s equilibrium by being a significant link in the food chain.
Adaptations For Survival
Rabbits have developed various adaptations to survive in the face of numerous predators. Their keen senses, speed, and burrowing abilities are essential for evading danger.
Mammalian Threats To Rabbits
Rabbits face threats from a range of predators including foxes, dogs, cats, birds of prey, and stoats. These animals hunt and eat rabbits, impacting their behavior, diet, and survival strategies. Rabbits primarily consume grasses and plants, with a digestive system adapted for high-fiber food.
Mammalian Threats to Rabbits
Rabbits are a common prey animal, and as such, they are hunted by many different mammalian predators. Some of the most common mammalian threats to rabbits include foxes, domestic and feral cats, dogs in the wild and at home, and mustelids such as stoats and weasels.
Foxes: Cunning Hunters
Foxes are known for their cunning hunting skills, and they are one of the most common predators of rabbits. Foxes are able to stalk their prey silently and quickly, making them difficult for rabbits to detect. Once a fox has located a rabbit, it will often chase it down and kill it quickly.
Domestic And Feral Cats
Domestic and feral cats are also common predators of rabbits. Cats are natural hunters, and they have sharp claws and teeth that they use to catch and kill their prey. Domestic cats that are allowed to roam freely outside can pose a threat to wild rabbits, while feral cats are a major threat to rabbits in many areas.
Dogs In The Wild And At Home
Dogs that are allowed to roam freely in the wild can also pose a threat to rabbits. Many breeds of dogs have a natural instinct to hunt small animals, and rabbits are often among their prey. Even dogs that are kept as pets can pose a threat to rabbits if they are not properly supervised and trained.
Mustelids: Stoats And Weasels
Mustelids, including stoats and weasels, are small, agile predators that are capable of catching and killing rabbits. These animals are known for their speed and agility, and they are able to slip through tight spaces and sneak up on their prey. Once a mustelid has caught a rabbit, it will often kill it quickly with a bite to the neck.
In conclusion, rabbits face many threats from mammalian predators, including foxes, cats, dogs, and mustelids. These predators are skilled hunters that are capable of catching and killing rabbits quickly and efficiently. As a prey animal, rabbits must constantly be on the lookout for danger and be ready to flee at a moment’s notice.
Birds Of Prey: Aerial Predators
When it comes to hunting rabbits, birds of prey, also known as raptors, play a crucial role as aerial predators. These magnificent hunters rely on their keen eyesight, powerful talons, and sharp beaks to capture their prey.
Hawks And Eagles
Hawks and eagles are formidable hunters that soar high in the sky, scanning the ground below for potential prey. With exceptional vision, they can spot rabbits from great distances. Once they lock onto their target, they swoop down with incredible speed and precision, using their sharp talons to grasp the unsuspecting rabbit.
Owls: Silent Nocturnal Hunters
Owls are renowned for their silent flight and nocturnal hunting prowess. Under the cover of darkness, these stealthy predators rely on their acute hearing to detect the faintest rustle of a rabbit’s movements. With swift and silent precision, they swoop down on their unsuspecting prey, using their powerful talons to secure a successful hunt.
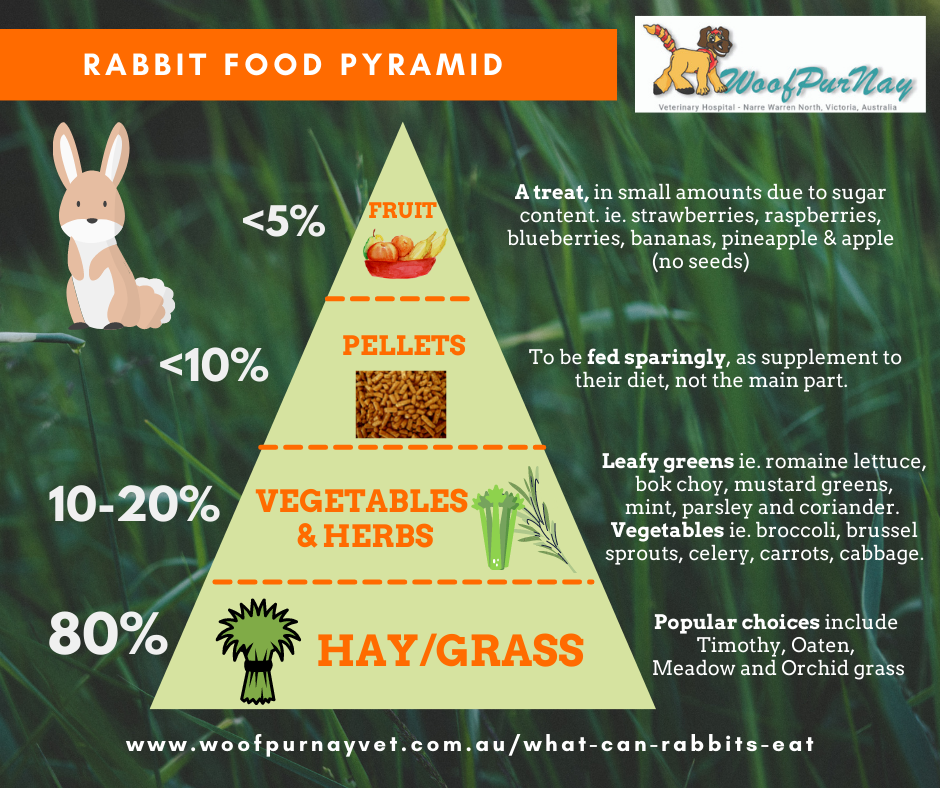
Credit: www.woofpurnayvet.com.au
Reptilian And Amphibian Predators
Rabbits are prey to a variety of predators, including reptiles and amphibians. Let’s explore some of the reptilian and amphibian predators that pose a threat to rabbits.
Snakes: Stealthy Predators
Snakes are stealthy predators that pose a significant threat to rabbits. Their ability to slither into rabbit burrows or ambush them in the open makes them formidable hunters. Some of the snake species known to prey on rabbits include rat snakes, gopher snakes, and king snakes.
Large Frogs And Toads
While not as common as snakes, large frogs and toads also pose a threat to rabbits, especially in wetland and marshy habitats. Species such as bullfrogs and cane toads have been known to prey on young or small rabbits when given the opportunity.
Aquatic Predators: Unseen Dangers
Rabbits face threats not only on land but also from aquatic predators. It may come as a surprise that various creatures from the water pose a danger to these small, furry creatures.
Fish: Unexpected Predators
While it’s common knowledge that birds of prey and land-dwelling predators hunt rabbits, fish are often overlooked as potential threats. Certain species of fish, such as pike and muskie, are known to prey on rabbits that come near the water’s edge. These fish possess sharp teeth and lightning-fast reflexes, making them formidable hunters in aquatic environments.
Otters And Minks
Otters and minks, with their sleek and agile bodies, are skilled hunters both on land and in water. These aquatic mammals are known to hunt rabbits that venture near rivers, streams, or marshy areas. Their speed and stealth enable them to catch rabbits by surprise, making them a significant threat to the rabbit population in aquatic habitats.
Human Impact On Rabbit Predation
Humans have a significant impact on the predation of rabbits through their hunting practices and habitat alteration.
Hunting Practices
Humans, as predators, have historically hunted rabbits for various reasons including food, fur, and sport. This hunting activity has contributed to a reduction in the rabbit population in some areas, particularly when not properly regulated. The introduction of non-native predators by humans, such as domestic cats and dogs, has also increased the predation pressure on rabbits.
Habitat Alteration
The alteration of natural habitats by human activities, such as urbanization, agriculture, and deforestation, has had a direct impact on the availability of suitable habitats for rabbits. This has led to a decrease in the population of rabbits in these areas, as well as an increase in predation by other animals that thrive in the altered environments.
Rabbits As Prey: Ecological Implications
Rabbits are prey for various predators such as foxes, dogs, cats, birds of prey, and stoats. These predators influence the rabbits’ behavior, diet, and communication patterns. Rabbits mainly eat grasses and plants, with their teeth and digestive system adapted for high-fiber foods.
Population Control
Rabbits are known for their high reproductive rate. In some areas, rabbit populations can grow very quickly and become a problem. This is where the role of predators comes in. Predators such as foxes, dogs, cats, birds of prey, and stoats help control the rabbit population by hunting and eating them. This ensures that the rabbit population doesn’t grow too large, which can have negative impacts on the ecosystem.
Ecosystem Balance
The presence of rabbits in an ecosystem can have both positive and negative impacts. On one hand, they help maintain the balance of the ecosystem by providing a food source for predators. On the other hand, an overabundance of rabbits can have negative effects on the ecosystem. They can overgraze on plants, which can lead to soil erosion, and their burrows can cause damage to the landscape. However, with the help of predators, the rabbit population is kept in check, which helps maintain the balance of the ecosystem.
In conclusion, rabbits play an important role in the ecosystem as prey animals. Their high reproductive rate makes them a valuable food source for predators, which helps control their population and maintain the balance of the ecosystem. Predators play a crucial role in population control and ecosystem balance, ensuring that the rabbit population doesn’t grow too large and cause negative impacts.

Credit: be.chewy.com
Protecting Rabbits: Conservation Efforts
Rabbits face threats from various predators in the wild, making conservation efforts crucial to their survival. By implementing measures such as creating sanctuaries and enforcing legal protections, we can help safeguard these vulnerable creatures.
Sanctuaries And Rescues
Sanctuaries and rescues play a vital role in protecting rabbits from harm. These organizations provide a safe haven for rabbits that have been injured, orphaned, or displaced, offering them a chance to recover and thrive in a secure environment. By supporting sanctuaries and rescues, we can contribute to the well-being of these precious animals.
Legal Protections And Regulations
Legal protections and regulations are essential for safeguarding rabbits from threats such as habitat destruction and poaching. Laws that prohibit hunting or trapping of rabbits help ensure their populations remain stable and sustainable. By enforcing these regulations, authorities can deter illegal activities that endanger the lives of rabbits.
Conclusion: The Complex Web Of Predation
Rabbits face a wide range of predators such as foxes, dogs, cats, birds of prey, and stoats. This influences their diet, behavior, and survival strategies in the complex web of predation.
Summary Of Rabbit Predators
Rabbits are prey animals with a wide range of predators, including foxes, dogs, cats, birds of prey, stoats, raccoons, and even some dog breeds trained for hunting. These predators impact the behavior, diet, and survival strategies of rabbits, shaping their natural habits and instincts.
The Importance Of Biodiversity
The complex web of predation involving rabbits and their predators highlights the importance of biodiversity in maintaining ecological balance. Each species plays a crucial role in the food chain, and the presence of diverse predators ensures that no single species becomes overly dominant, safeguarding the overall health of the ecosystem.

Credit: earthlife.net
Frequently Asked Questions
Which Animals Eat Rabbits?
Rabbits are hunted by foxes, dogs, cats, birds of prey, and stoats due to being prey animals.
Do Raccoons Eat Rabbits?
Yes, raccoons are predators and they hunt small mammals like rabbits as part of their diet.
What Food Eats Rabbits?
Rabbits eat grasses and plants as their main diet. They need high-fiber food like hay for digestion.
What Will Hunt A Rabbit?
Rabbits are prey animals and are hunted by a variety of predators, including foxes, dogs, cats, birds of prey, and stoats. Dogs, particularly beagles, are commonly used for hunting rabbits. Rabbits primarily eat grasses and other plants, and their digestive system is designed for high fiber, low-quality food.
Some predators, such as raccoons, also hunt small mammals like rabbits.
Conclusion
Rabbits are prey to various predators such as foxes, dogs, cats, birds of prey, and stoats. Their diet mainly consists of grasses and plants. Understanding their predators impacts how they eat, communicate, and behave in their environment. These factors play a crucial role in the rabbit’s survival.