A cow can cost anywhere from $500 to $3,000, depending on factors such as breed, age, and location. Cattle prices can vary greatly, so it’s essential to research and compare prices before making a purchase.
If you’re considering buying a cow, it’s important to understand the various factors that can influence the price. The breed of the cow plays a significant role, with some breeds being more expensive than others due to their desirable traits or high demand.
Age is another crucial factor, as younger cows are generally more expensive than older ones. Additionally, the location where you’re buying the cow can affect the price, as costs can vary depending on local market conditions and transportation expenses. Before making a decision, it’s advisable to consult with local farmers or livestock experts to get an accurate estimate of the current market prices in your area. By doing thorough research and comparing prices, you can ensure that you’re getting a fair deal when purchasing a cow.
The Value Of Cattle: More Than Just Money
When we think of cattle, the first thing that comes to mind is money. After all, cows are commonly bought and sold for their meat, milk, and other products. But the value of cattle goes beyond just monetary gain. In this article, we’ll explore the cultural significance and economic impact of cows.
Cultural Significance
Cows have played an important role in many cultures throughout history. In Hinduism, cows are considered sacred and are often seen roaming freely in the streets. In some African societies, cows are a symbol of wealth and are used as a form of currency. The Maasai tribe of Kenya and Tanzania, for example, measure their wealth in terms of the number of cows they own.
But beyond their role as a symbol of wealth, cows have also been a source of inspiration for art and literature. From ancient cave paintings to modern-day novels, cows have been depicted in various forms of creative expression.
Economic Impact
The economic impact of cattle is undeniable. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, there are approximately 1.5 billion cows in the world, and the global livestock industry is worth over $1 trillion.
In addition to the direct income generated from the sale of meat, milk, and other products, the cattle industry also creates jobs and supports local economies. From farmers and ranchers to veterinarians and meat processors, the industry provides employment opportunities for millions of people.
Furthermore, cows play a vital role in sustainable agriculture. They help to fertilize soil, control weeds, and even reduce greenhouse gas emissions through their manure.
Cows are more than just a source of income. They are a cultural icon and a vital part of our global economy. Whether you’re a farmer in rural America or a city-dweller on the other side of the world, the value of cattle is undeniable.
Breed Variations And Pricing
Understanding breed variations is essential when determining the pricing of cows. Dairy vs. Beef Cattle and High-Demand Breeds play a crucial role in the overall cost.
Dairy Vs. Beef Cattle
Dairy cattle are typically more expensive due to higher milk production rates. Beef cattle are priced based on their meat quality.
High-demand Breeds
- Angus: Known for marbling, priced higher for beef production.
- Jersey: Excellent milk production, higher price for dairy purposes.
- Hereford: Versatile breed, moderate pricing for both dairy and beef.
The pricing of cows varies based on breed characteristics and market demand. Breed selection impacts overall costs significantly.
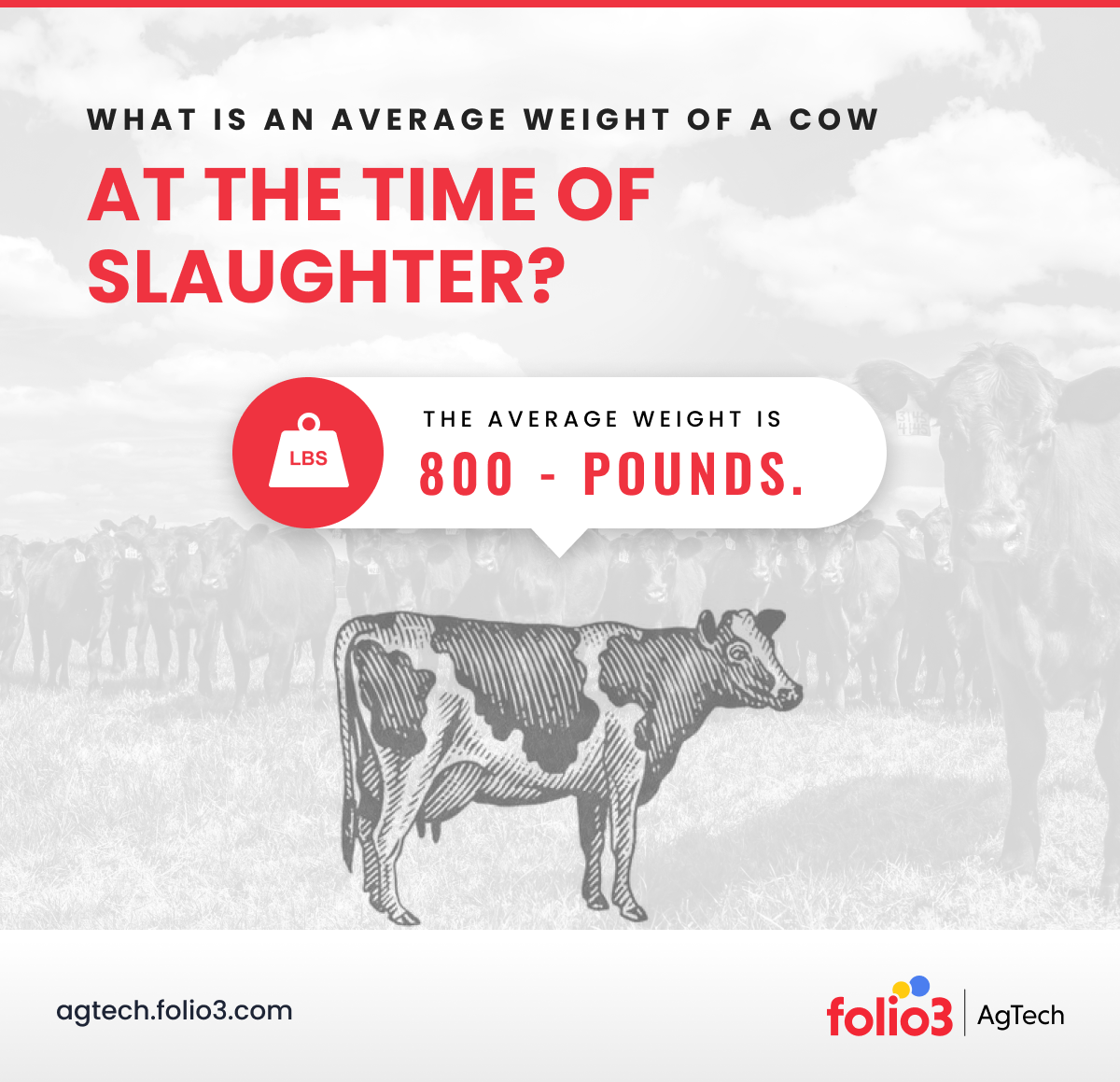
Age And Weight: Crucial Factors In Valuation
When it comes to determining the value of a cow, age and weight play a crucial role. These two factors not only affect the market price of the cow but also provide insights into its potential for various purposes, such as breeding, meat production, or milk yield.
Young Calves Vs. Mature Cows
Young calves and mature cows hold different values in the cattle market. While young calves are typically less expensive due to their size and limited potential for immediate production, they offer long-term value as they grow and develop. Investing in young calves allows for the opportunity to raise them into productive cows that can provide milk or offspring.
Mature cows, on the other hand, are often priced higher due to their immediate production capabilities. These cows have already reached their peak weight and are ready for breeding or milk production. The market price of a mature cow depends on factors such as breed, health, and productivity history.
Weight Categories And Their Market Prices
Weight is a crucial factor in determining the value of a cow. How Much is a Cow? Cattle are typically categorized into weight ranges, with each range having its own market price. Here are some common weight categories and their corresponding market prices:
| Weight Category | Market Price |
|---|---|
| Under 500 pounds | $X per pound |
| 500 – 800 pounds | $Y per pound |
| 800 – 1,200 pounds | $Z per pound |
| Over 1,200 pounds | $A per pound |
The market prices mentioned above are subject to fluctuation due to factors such as supply and demand, breed, quality, and location. It’s important to stay updated with the current market trends and consult local experts or livestock agents to get accurate valuations.
Understanding the relationship between age, weight, and valuation is essential for anyone involved in the cattle industry. Whether you are buying or selling cows, considering these crucial factors will help you make informed decisions and ensure fair pricing.
Location And Market Fluctuations
When it comes to buying a cow, the price can vary significantly depending on several factors. One of the most significant factors is the cow’s location and market fluctuations. This article will discuss the regional price differences and seasonal trends in cattle trade that affect how much a cow costs.
Regional Price Differences
The price of a cow can vary depending on the region in which it is bought. For example, in the United States, cows in the Midwest region may be cheaper than those in the Northeast region due to differences in supply and demand. Similarly, cows in rural areas may be less expensive than those in urban areas due to the cost of transportation and other factors.
A table of regional price differences in the United States:
| Region | Average Price per Cow |
|---|---|
| Midwest | $1,200 – $1,500 |
| Northeast | $1,500 – $2,000 |
| South | $1,000 – $1,500 |
| West | $1,500 – $2,000 |
Seasonal Trends In Cattle Trade
The price of a cow can also vary depending on the season. Seasonal trends in cattle trade can affect the supply and demand of cows, which can impact the price. For example, during the fall months, the demand for cows may increase due to the holiday season, which can result in higher prices.
Here are some seasonal trends in cattle trade:
- Cows are typically more expensive in the fall due to increased demand for holiday feasts.
- Cows are typically less expensive in the spring due to increased supply from calving season.
- Cows are typically more expensive during droughts, as the supply of cattle feed decreases.
- Cows are typically less expensive during periods of overproduction, as the supply of cows increases.
Understanding the regional price differences and seasonal trends in cattle trade can help you make an informed decision when it comes to buying a cow. It’s essential to research the market in your area and consider the factors that may impact the price.
The Role Of Genetics In Cattle Valuation
Purebreds And Pedigrees
When evaluating the value of cattle, the consideration of genetics plays a pivotal role. Purebred cattle, which are animals of a known and documented ancestry, often command higher prices due to their predictable traits and performance. These animals are typically the result of selective breeding to maintain specific genetic characteristics within a breed.
Genetic Traits And Their Worth
Genetic traits such as growth rate, feed efficiency, disease resistance, and maternal ability significantly impact the value of cattle. Cattle with desirable genetic traits are more productive and efficient, leading to greater profitability for producers. Buyers are willing to pay a premium for cattle with superior genetics that contribute to improved herd performance and overall profitability.
Credit: agtech.folio3.com
Investment In Health: Vaccinations And Veterinary Care
When it comes to owning a cow, it’s important to prioritize their health and well-being. This not only ensures the longevity and happiness of the animal but also has a direct impact on their value in the market. Investing in vaccinations and veterinary care is essential for maintaining the overall health of your cow and maximizing its potential.
Routine Health Maintenance Costs
Regular health maintenance for your cow involves various costs that are necessary for their overall well-being. These costs may include:
- Vaccinations: Vaccinations play a crucial role in preventing diseases and protecting your cow from potential health risks. Common vaccinations for cows include those for diseases like bovine viral diarrhea, infectious bovine rhinotracheitis, and bovine respiratory syncytial virus.
- De-worming: Regular de-worming treatments help control internal parasites that can negatively impact the health and productivity of your cow. Parasite control is vital to ensure proper digestion and nutrient absorption.
- Hoof care: Maintaining healthy hooves is essential for the mobility and comfort of your cow. Regular hoof trimming and treatment for common hoof ailments like foot rot or laminitis may be necessary.
- Nutritional supplements: Providing your cow with appropriate nutritional supplements ensures they receive a balanced diet and have all the necessary vitamins and minerals for optimal health.
Impact Of Health On Sale Price
The health and condition of your cow can significantly impact its sale price. Buyers are more likely to invest in a healthy cow that shows no signs of illness or disease. A well-maintained cow with a clean bill of health is not only more appealing to potential buyers but also has a higher market value.
Additionally, a healthy cow is more likely to have better reproductive performance, leading to increased productivity and potentially higher profits. By investing in the health of your cow, you are not only ensuring their well-being but also enhancing their value as an asset.
In conclusion, prioritizing vaccinations and veterinary care for your cow is a wise investment. It not only safeguards their health but also increases their market value. Regular health maintenance costs, including vaccinations, de-worming, hoof care, and nutritional supplements, are essential for optimal cow health. Remember, a healthy cow is a valuable cow.
The Economics Of Feeding: Input Costs Vs. Output Gains
The economics of feeding a cow involves balancing input costs with output gains to determine its total worth. Understanding the cost of raising a cow is essential for farmers to maximize profits and ensure sustainable livestock management practices.
Cow farming involves managing input costs for feeds against the resulting output gains. Let’s delve into the specifics to understand the dynamics better.
Feed Types And Their Costs
Nutrition’s Effect On Growth And Value
Nutrition directly impacts a cow’s growth and overall value. – Balanced diet boosts weight gain – Quality feed enhances market price
Credit: www.quora.com
Sustainability And Ethical Farming Practices
Discover the true cost of a cow and the importance of sustainable and ethical farming practices. Explore how these practices contribute to a healthier environment, higher quality meat, and a more responsible approach to animal welfare. Experience the benefits of supporting farms that prioritize sustainability and ethical practices.
Consumer Demand For Ethical Products
Sustainability and Ethical Farming Practices are crucial in the cattle industry. Farmers focus on organic methods and grass-fed diets to promote sustainable practices. Consumers increasingly seek ethically produced beef. Organic and grass-fed cattle often command higher prices due to premium quality. Farmers adhere to strict standards for organic certification. Grass-fed cows lead to healthier animals and environmentally friendly practices. Consumers are driving the market towards ethical products. They prefer beef from farms with transparent and humane practices. Farmers strive to meet this demand through sustainable and ethical farming practices. Ethical farming practices are essential for sustainability and meeting consumer demands.
Future Trends In Cattle Pricing
In the dynamic world of agriculture, staying informed about future trends in cattle pricing is crucial for farmers and industry stakeholders. With advancements in technology and market forecasting, the landscape of cattle pricing is evolving rapidly.
Technological Advancements In Farming
Technology continues to revolutionize the farming industry, impacting cattle pricing as well. Innovations such as smart farming tools and precision agriculture techniques are enhancing efficiency and productivity in cattle production.
Predicting Market Changes
Accurately predicting market changes is vital for navigating the volatility of cattle pricing. Utilizing data analytics and machine learning algorithms can provide valuable insights into market trends and price fluctuations.

Credit: ranchr.ag
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Average Cost Of A Cow?
The average cost of a cow can vary depending on factors such as breed, age, and market demand. Generally, the cost can range from $1,000 to $2,500 for a dairy cow, while beef cattle can range from $1,200 to $2,500.
How Much Space Does A Cow Need?
Cows typically require 2 to 5 acres of pasture land for grazing and exercise. Adequate space is essential for their physical and mental well-being, ensuring they have access to fresh grass, water, and shelter.
What Are The Ongoing Expenses Of Owning A Cow?
Ongoing expenses for cow ownership include feed, veterinary care, and maintenance of fencing and shelter. Additionally, costs may arise for breeding services, vaccinations, and potential emergency medical care. It’s important to budget for these ongoing expenses when considering cow ownership.
Conclusion
The cost of a cow varies based on factors like breed, age, and market demand. Whether for dairy or beef production, owning a cow is a long-term investment. Understanding the expenses involved is crucial for farmers and enthusiasts alike. Research and preparation are key to successful cow ownership.