Suboxone can be detected in your system for up to 2-9 days after the last dose. Its duration varies based on metabolism and individual factors.
Suboxone, a medication used to treat opioid dependence, can be detected in the body for a period of 2 to 9 days after the last dose. This duration may vary depending on factors such as metabolism and individual differences. Understanding how long Suboxone stays in the system is important for individuals undergoing drug testing or considering changes to their medication regimen.
Whether you are a healthcare professional, patient, or have a loved one undergoing Suboxone treatment, knowing the duration of its presence in the body can provide valuable insight into its effects and potential interactions. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the factors that influence the detection window of Suboxone in the body and its implications.
Introduction To Suboxone
Suboxone is a medication primarily used to treat opioid addiction. It’s a combination of two active ingredients: buprenorphine and naloxone. Buprenorphine is a partial opioid agonist, which means it activates the same receptors in the brain as other opioids, such as heroin or prescription painkillers. However, it produces a weaker effect, which helps reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms. Naloxone, on the other hand, is an opioid antagonist, which means it blocks the effects of opioids. It’s added to Suboxone to discourage misuse and abuse of the medication.
The Role Of Suboxone In Opioid Dependence
Suboxone is often used as part of a comprehensive treatment program for opioid dependence. It helps reduce withdrawal symptoms and cravings, which can make it easier for individuals to stop using opioids. Suboxone is also used as a maintenance medication, meaning it’s taken over a longer period to help prevent relapse. However, it’s important to note that Suboxone isn’t a cure for opioid addiction. It’s just one tool in a larger treatment plan that may include counseling, therapy, and support groups.
Key Components Of Suboxone
As mentioned, Suboxone contains two active ingredients: buprenorphine and naloxone. The ratio of these ingredients can vary depending on the dosage strength. For example, Suboxone Film, which is a dissolvable film that’s placed under the tongue, comes in several strengths ranging from 2 mg/0.5 mg to 12 mg/3 mg. The exact dosage and duration of treatment will depend on the individual’s needs and the recommendation of their healthcare provider.
It’s important to take Suboxone exactly as prescribed and to follow all instructions carefully. Misusing or abusing Suboxone can lead to serious side effects, including respiratory depression, coma, or death. If you have any questions or concerns about Suboxone or its use, be sure to talk to your healthcare provider.
Pharmacokinetics Of Suboxone
How Long Does Suboxone Stay in Your System? Suboxone’s pharmacokinetics determine its presence in your system. The drug can be detected in urine for up to 2-4 days after the last dose. Factors like metabolism and dosage influence how long Suboxone stays in your body.
Suboxone is a medication that contains buprenorphine and naloxone. It is used to treat opioid addiction and works by reducing withdrawal symptoms and cravings. The pharmacokinetics of Suboxone refers to the way the drug is absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and eliminated by the body. Understanding how long Suboxone stays in your system is important for patients who are receiving treatment.
Absorption And Distribution
Suboxone is available in two forms: sublingual tablets and sublingual film. When taken as directed, the medication is absorbed into the bloodstream through the mucous membranes under the tongue. The absorption of Suboxone is relatively slow, with peak levels occurring within 1-4 hours of administration. The distribution of Suboxone is limited, as the drug does not cross the blood-brain barrier easily. This means that the effects of Suboxone are mostly localized to the site of administration.
Metabolism And Elimination
Once Suboxone is in the bloodstream, it is transported to the liver where it is metabolized. The liver breaks down buprenorphine into several metabolites, which are then eliminated from the body through the kidneys and feces. The half-life of Suboxone is approximately 24-42 hours, which means that it takes about that long for half of the drug to be eliminated from the body. However, the elimination of Suboxone can be affected by a number of factors, including liver function, kidney function, and body weight.
In conclusion, the pharmacokinetics of Suboxone are complex and involve multiple factors. While the half-life of the drug is relatively long, the effects of Suboxone are mostly localized to the site of administration. Patients who are receiving treatment with Suboxone should be aware of how long the drug stays in their system, as this can affect their ability to drive or operate machinery.
Factors Influencing Suboxone Retention
Individual Metabolism Variability
Genetic differences influence how long Suboxone stays in the system.
Dosage And Frequency Of Use
Higher doses and frequent use can extend Suboxone detection time.

Credit: www.palmerlakerecovery.com
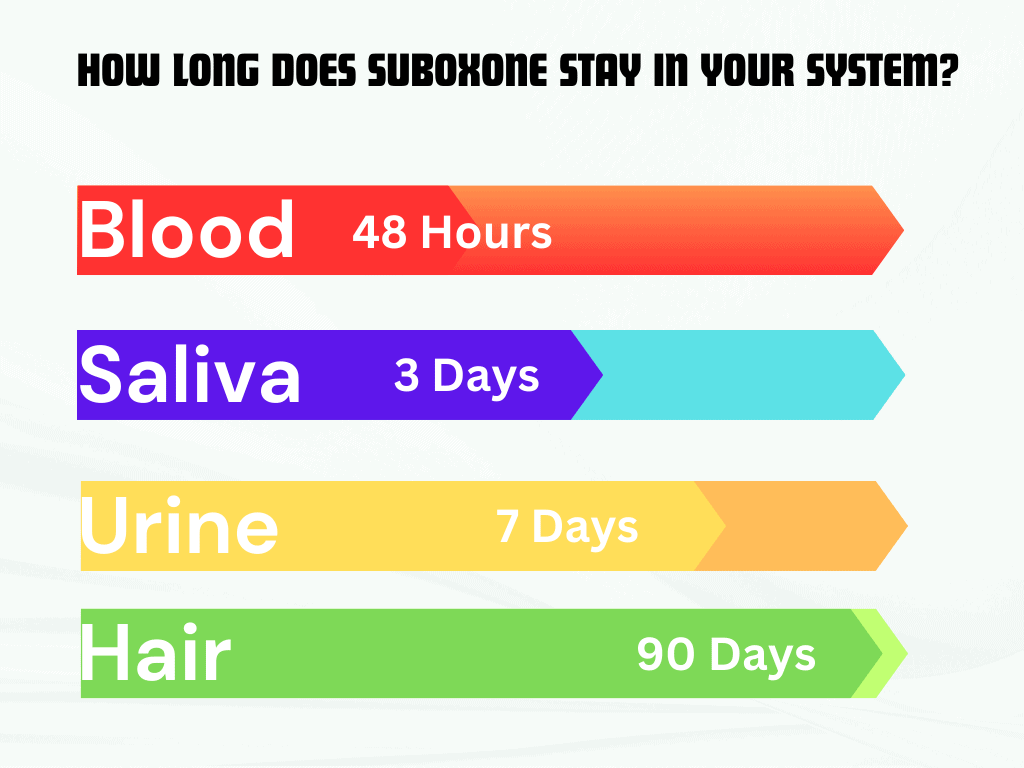
Detection Window Of Suboxone
Suboxone can be detected in the system for up to 2-10 days after the last dose. The detection window varies depending on factors such as metabolism, frequency of use, and dosage. It’s important to consult a healthcare professional for personalized guidance on Suboxone detection and its effects.
Urine Testing
When it comes to detecting Suboxone in your system, urine testing is one of the most common methods used. The detection window for Suboxone in urine typically ranges from 2 to 7 days after the last use. It’s important to note that individual factors such as metabolism, frequency of use, and dosage can affect the detection time.
Blood Testing
Blood testing is another method used to detect Suboxone in your system. The detection window for Suboxone in blood is relatively shorter compared to urine testing. Suboxone can be detected in the bloodstream for up to 24 hours after the last use. However, it’s essential to consider that blood testing is less commonly used for Suboxone detection.
Saliva Testing
Saliva testing is a less invasive method to detect Suboxone in your system. The detection window for Suboxone in saliva is similar to blood testing, lasting up to 24 hours after the last use. This type of testing is often preferred in situations where immediate or recent drug use needs to be determined.
Hair Follicle Testing
Hair follicle testing is a more extensive method for detecting Suboxone in your system. This testing method can provide a longer detection window compared to urine, blood, or saliva testing. Suboxone can be detected in hair follicles for up to 90 days after the last use. However, it’s important to note that hair follicle testing is less commonly used due to its higher cost and longer detection period.
Short-term Effects Of Suboxone
Suboxone, a medication used to treat opioid addiction, has short-term effects that can last for a few hours. The drug typically stays in your system for about 2-3 days, but this can vary depending on factors such as metabolism and dosage.
It’s important to follow your doctor’s instructions and seek professional guidance for any concerns.
Onset Of Action
After taking Suboxone, the onset of action typically occurs within 30 minutes to 2 hours. The active ingredients in Suboxone, buprenorphine, and naloxone, work together to bind to the opioid receptors in the brain, reducing cravings and withdrawal symptoms associated with opioid addiction. Buprenorphine has a high affinity for these receptors, allowing it to provide a long-lasting effect even at lower doses.
Duration Of Efficacy
The duration of efficacy for Suboxone can vary depending on factors such as the individual’s metabolism, dosage, and frequency of use. On average, Suboxone’s effects can last for approximately 24 to 72 hours. This extended duration of action is one of the reasons why Suboxone is commonly prescribed for opioid addiction treatment. It helps to stabilize individuals and reduce the need for frequent dosing, allowing them to focus on their recovery.
It is important to note that the duration of efficacy can also be influenced by how Suboxone is taken. When Suboxone is taken sublingually (placed under the tongue), the effects tend to last longer compared to when it is swallowed.
Suboxone’s long duration of efficacy provides individuals with a steady level of medication in their system, helping to manage withdrawal symptoms and cravings. This stability is crucial in the early stages of recovery, allowing individuals to work on their treatment plan and make positive changes in their lives.
In conclusion, understanding the short-term effects of Suboxone, including the onset of action and duration of efficacy, can help individuals undergoing opioid addiction treatment to have realistic expectations and better manage their recovery journey.
Potential Side Effects
When using Suboxone, it’s important to be aware of the potential side effects that may occur. These side effects can range from common adverse reactions to long-term health implications. Understanding these effects can help individuals make informed decisions about their treatment plan.
Common Adverse Reactions
Suboxone, like any medication, can cause common adverse reactions in some individuals. These may include nausea, headache, insomnia, constipation, and anxiety. It’s essential to consult a healthcare professional if these side effects persist or worsen.
Long-term Health Implications
Using Suboxone over the long term may have potential health implications. Some individuals may experience decreased libido, hormonal imbalances, and mood changes. Regular monitoring by a healthcare provider is crucial to address any emerging concerns and ensure overall well-being.
Withdrawal And Detoxification
Withdrawal from Suboxone can be challenging but is a necessary step towards recovery. The detoxification process involves managing symptoms and gradually eliminating the drug from the system.
Symptoms Of Suboxone Withdrawal
Common symptoms include nausea, sweating, anxiety, and muscle aches.
- Symptoms: Nausea, sweating, anxiety, muscle aches
Detox Timeline
The detox timeline varies but typically lasts 1-2 weeks, with symptoms peaking within the first 72 hours.
- Timeline: 1-2 weeks
- Symptom Peak: Within first 72 hours
Credit: www.recoverydelivered.com
Legal And Medical Considerations
Suboxone, a medication used to treat opioid addiction, can stay in your system for varying lengths of time. Factors such as dosage, frequency of use, and individual metabolism can affect the duration. Understanding the legal and medical considerations of Suboxone’s presence in your system is crucial for those undergoing treatment or facing drug tests.
Suboxone, a medication used to treat opioid addiction, raises important legal and medical considerations. Understanding the Prescription Regulations and the classification of Suboxone as a Controlled Substance is crucial.
Prescription Regulations
When prescribing Suboxone, healthcare providers must adhere to strict guidelines. Patients require a prescription from a licensed medical professional to obtain this medication legally.
Suboxone As A Controlled Substance
Suboxone is classified as a Schedule III controlled substance. This designation indicates that while it has medical benefits, there is also a potential for abuse and dependence.
Faqs About Suboxone Use
Suboxone can typically stay in your system for about 2-4 days after the last dose. Factors like metabolism and dosage can affect how long it remains detectable. It’s essential to consult a healthcare provider for personalized information on Suboxone use and its duration in your system.
Safe Usage Guidelines
Follow prescribed dosage for safe use.
Avoid alcohol while taking Suboxone.
Do not crush or chew Suboxone tablets.
Interactions With Other Medications
Avoid mixing Suboxone with benzodiazepines.
Consult doctor before taking other medications.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Long Does Suboxone Stay In Your System?
Suboxone can be detected in urine for up to 2-3 days, in blood for up to 24 hours, and in saliva for up to 5-7 days. However, the duration may vary based on factors such as metabolism and dosage.
What Factors Affect The Duration Of Suboxone In The System?
Metabolism, frequency of use, hydration levels, and liver function can impact how long Suboxone stays in the system. Higher doses and prolonged use may lead to a longer detection window.
Can Suboxone Show Up In A Drug Test?
Yes, Suboxone can appear in drug screenings. It is essential to inform the testing facility about any prescribed medications, including Suboxone, to avoid any misinterpretation of the results. Always follow the advice of a healthcare professional.
How Does The Body Metabolize Suboxone?
After consumption, Suboxone is metabolized by the liver, primarily into norbuprenorphine. The metabolites are then excreted through urine and feces. Metabolism rates can vary among individuals. Consulting a healthcare provider is recommended.
Conclusion
Understanding how long Suboxone stays in your system is crucial for those undergoing treatment or being tested. The duration can vary based on factors such as dosage, frequency of use, and individual metabolism. By being aware of this information, individuals can better plan for their recovery journey and ensure compliance with drug tests.
Remember, it’s always best to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance.