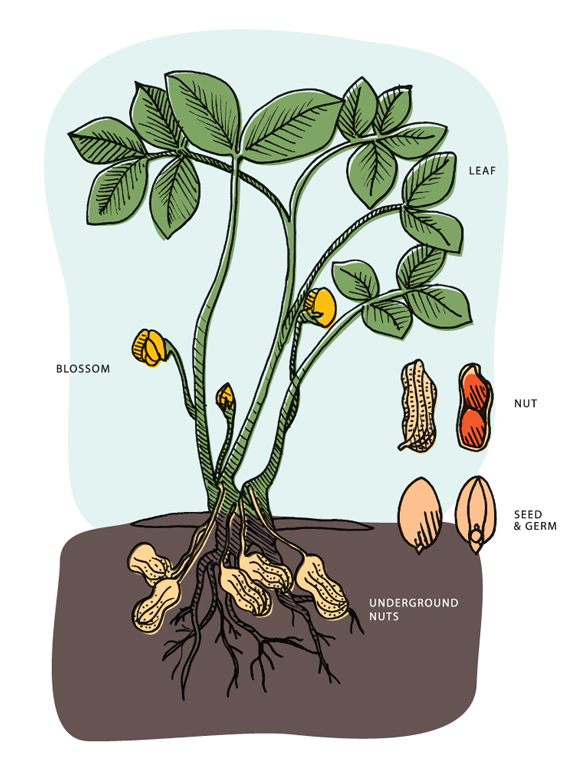
Peanuts grow underground, with the seeds forming inside the shells after the flowers are pollinated. Peanuts are legumes that belong to the Fabaceae family, and they require warm temperatures and well-drained soil to thrive.
These plants develop yellow flowers that self-pollinate, and after pollination, the flowers’ stems will elongate and bend towards the ground. The fertilized ovary then burrows into the soil, where the peanut pods mature. The process typically takes around 120 to 150 days, depending on the variety.
Once the pods are ready for harvest, the plants are uprooted, and the peanuts are separated from the plants and dried before being processed or consumed.
The Botanical Profile Of Peanuts
Peanuts, scientifically known as Arachis hypogaea, are fascinating legumes that have a unique botanical profile. Understanding the botanical aspects of peanuts can provide valuable insights into their growth and cultivation. In this section, we will delve into the botanical profile of peanuts, including their plant classification and distinctive features.
Peanut Plant Classification
The peanut plant belongs to the Fabaceae family, which is also referred to as the Leguminosae family. Within this family, it falls under the subfamily Faboideae. The botanical name for peanuts is Arachis hypogaea, highlighting its genus and species. This classification places peanuts among the diverse group of leguminous plants, known for their nitrogen-fixing abilities and economic significance.
Distinctive Features Of The Peanut Plant
- Peanut plants are low-growing, herbaceous annuals.
- They have compound leaves, consisting of four leaflets.
- Peanut flowers are unique, with a yellow color and a distinct shape.
- After pollination, the flowers develop into “pegs,” which elongate and eventually bury themselves in the ground to form the peanut pods.
These distinctive features contribute to the remarkable adaptation of peanut plants to their growth environment, making them a remarkable crop with a fascinating botanical profile.
Peanut Lifecycle Stages
How Do Peanuts Grow? Peanuts grow in four main stages: planting seeds, flowering, peg penetration, and pod development. The process involves careful cultivation and optimal conditions for each stage to ensure a successful peanut harvest.
Peanuts are a popular snack that is enjoyed all over the world. But have you ever wondered how peanuts grow? The peanut plant goes through several stages in its lifecycle, from germination to pod development. Let’s take a closer look at each of these stages.
Germination
The first stage in the lifecycle of a peanut plant is germination. This is when the seed begins to sprout and grow roots. The peanut seed needs warm soil to germinate, so it is typically planted in the spring. Once the seed has germinated, it will continue to grow roots and a shoot.
Vegetative Growth
During the vegetative growth stage, the peanut plant will continue to grow leaves and stems. This stage can last for several weeks, depending on the climate and growing conditions. The peanut plant needs plenty of sunlight and water to grow during this stage.
Flowering And Pollination
The flowering and pollination stage is when the peanut plant begins to produce flowers. These flowers are yellow in color and are produced on long stalks. The flowers are pollinated by bees and other insects, which transfer pollen from the male flowers to the female flowers.
Pegging And Pod Development
The final stage in the lifecycle of a peanut plant is pegging and pod development. During this stage, the plant produces pegs, which are small stems that grow down from the flowers and into the soil. The pegs will eventually develop into pods, which contain the peanuts. The pods will continue to grow and mature until they are ready to be harvested.
In conclusion, the peanut plant goes through several stages in its lifecycle, from germination to pod development. Each stage is important for the growth and development of the plant, and each stage requires the right growing conditions to be successful. By understanding the lifecycle of the peanut plant, we can appreciate the hard work that goes into producing this popular snack.
Optimal Conditions For Peanut Cultivation
Peanuts grow best in warm climates with well-drained soil and plenty of sunlight. They require about 120-150 days to reach maturity. Adequate water and regular weeding are crucial for optimal peanut cultivation.
Soil Requirements
Peat is not suitable for peanuts due to poor aeration.
Climate And Temperature
Warmth is essential for peanut growth and development.
Watering Needs
Consistent moisture levels are crucial for healthy peanut plants. Optimal conditions for peanut cultivation involve specific requirements to ensure successful growth. Peanuts thrive in well-drained soil with good aeration. Peat is not suitable for peanuts due to poor aeration. Warmth is essential for peanut growth and development. Consistent moisture levels are crucial for healthy peanut plants.

Credit: www.thetreecenter.com
Planting Practices For Peanuts
When it comes to growing peanuts, proper planting practices play a crucial role in ensuring a successful crop. From preparing the soil to implementing effective seeding techniques and row spacing strategies, each step contributes to the overall growth and yield of peanuts. In this article, we will explore the essential considerations for planting peanuts and how they can be optimized for optimal results.
Preparation Of The Soil
Before planting peanuts, it is important to prepare the soil adequately. This involves several key steps:
- Clear the area of any existing vegetation or debris to create a clean and weed-free space for planting.
- Perform a soil test to determine its pH level and nutrient composition. Peanuts thrive best in slightly acidic soil with a pH range of 5.8 to 6.2.
- Based on the soil test results, amend the soil with appropriate fertilizers and organic matter to ensure optimal nutrient levels.
- Loosen the soil using a tiller or garden fork to improve its texture and allow for better root penetration.
Seeding Techniques
When it comes to seeding peanuts, there are a few techniques that can enhance germination and overall plant growth:
- Use high-quality peanut seeds that are free from diseases and have a high germination rate.
- Plant the seeds at a depth of approximately 1 to 2 inches, ensuring they are evenly spaced and not overcrowded.
- Consider using a seed inoculant, which contains beneficial bacteria that help fix nitrogen in the soil and promote healthier plant growth.
- Ensure the seeds are adequately watered immediately after planting to facilitate germination.
Row Spacing Strategies
Proper row spacing is crucial for peanuts to maximize their growth potential and yield. Consider the following strategies:
| Row Spacing | Advantages |
|---|---|
| Narrow Spacing (10-12 inches) |
|
| Wide Spacing (36-42 inches) |
|
By implementing these row spacing strategies, farmers can tailor their approach based on their specific needs and environmental conditions.
The Unique Reproductive Process
Self-pollination Explained
Peanuts have a fascinating reproductive process. Self-pollination is the key to their unique growth. The flowers of the peanut plant, known as pistillate flowers, are self-pollinating. This means that the plant can fertilize itself without the need for external pollinators. The process begins with the mature pistil, which elongates and curves until it touches the stamen. This allows the plant to pollinate itself, leading to the development of the peanut pod.
The Phenomenon Of Geocarpy
One of the most intriguing aspects of peanut growth is the phenomenon of geocarpy. This is a unique process where the peanut plant actually buries its own seeds. After self-pollination, the peanut flower’s ovary elongates and forms a structure called a peg. The peg then grows downward, burying itself in the soil where the peanut pod will mature. This remarkable adaptation ensures that the developing peanuts are protected and provided with the ideal environment for growth.
Growth Challenges And Pest Management
Peanuts face growth challenges and require effective pest management. Understanding how peanuts grow is crucial for successful cultivation, as it helps farmers implement appropriate pest control measures to ensure healthy plant growth and maximize yields.
Common Pests And Diseases
Peanuts, like any other crop, face several challenges when it comes to growth and are susceptible to various pests and diseases. Let’s take a closer look at some of the common pests and diseases that can affect peanut plants. One of the most common pests that affect peanuts is the tomato spotted wilt virus (TSWV). This virus is transmitted by thrips, tiny insects that feed on the plant’s leaves. TSWV can cause stunted growth, yellowing of leaves, and even death in severe cases.
To prevent the spread of this virus, farmers often employ integrated pest management techniques. Another pest that poses a threat to peanut crops is the peanut root-knot nematode. These microscopic worms infect the roots of the plant, causing the formation of galls or knots. This leads to reduced nutrient uptake, stunted growth, and lower yields. Crop rotation, soil sterilization, and resistant varieties are some methods used to manage this pest.
Integrated Pest Management
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a holistic approach to pest control that focuses on minimizing the use of pesticides while effectively managing pests. It involves combining various pest control methods to maintain pest populations below economically damaging levels. IPM strategies include: 1. Cultural Practices: Implementing practices like crop rotation, proper irrigation, and maintaining optimal planting density can help reduce pest pressure. 2. Biological Control:
Encouraging the presence of natural enemies like beneficial insects, spiders, and nematodes that prey on pests can help control their populations. 3. Chemical Control: When necessary, judicious use of pesticides can be employed. However, it is important to choose the right pesticide, apply it at the correct time, and follow label instructions to minimize environmental impact. 4. Monitoring and Thresholds: Regular scouting of fields to monitor pest populations is essential.
By setting action thresholds based on pest levels, farmers can determine when intervention is necessary. Implementing an integrated pest management approach not only helps in controlling pests effectively but also minimizes the impact on the environment and promotes sustainable farming practices. In conclusion, peanuts face several growth challenges and are vulnerable to various pests and diseases. By being aware of common pests and diseases, and adopting integrated pest management strategies, farmers can successfully protect their peanut crops and ensure optimal growth and yield.
Harvesting Peanuts
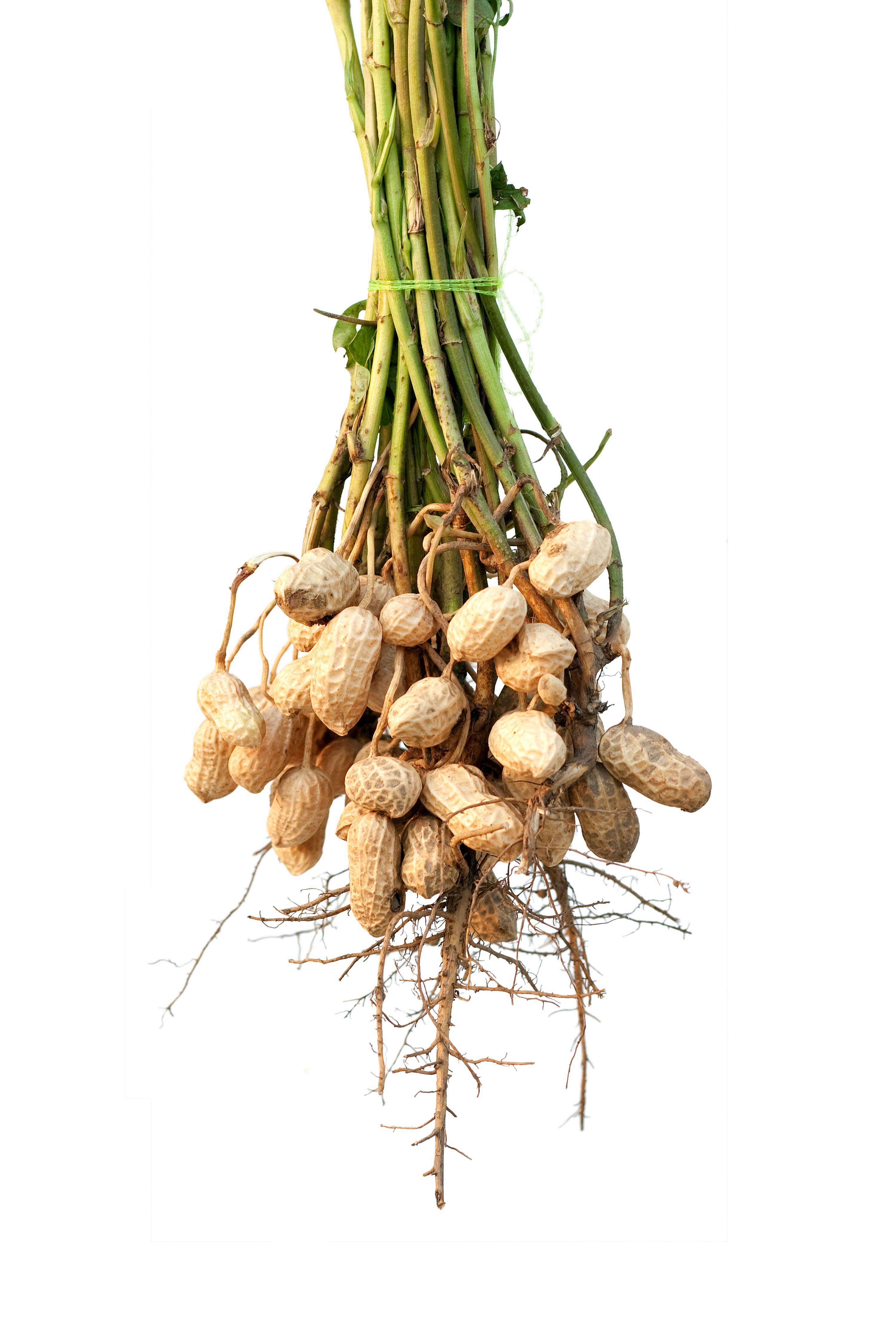
Peanuts grow underground and are ready for harvesting when the leaves turn yellow. The peanuts are carefully dug up and left to dry before being picked to prepare for consumption or processing.
Determining Harvest Time
Peanuts are ready to harvest when the leaves of the plant turn yellow and start to wither.
Digging And Gathering
Farmers use special equipment to carefully dig up the peanut plants from the ground.
Drying And Curing
The freshly harvested peanuts are laid out to dry in the sun before being cured for storage.

Credit: www.countryliving.com
From Farm To Table
Post-harvest Processing
Peanuts undergo drying, shelling, and sorting after harvest.
The nuts are then cleaned, roasted, and packaged for distribution.
Peanuts In The Market
Peanuts are sold as raw nuts, roasted snacks, or as peanut butter.
They are available in grocery stores, markets, and online platforms.
Uses And Products
- Peanuts are used in cooking, baking, and as a source of oil.
- Common products include peanut butter, oil, and flour.
Credit: www.flpeanuts.com
Frequently Asked Questions
How Are Peanuts Grown?
Peanuts grow underground in sandy soil, unlike other nuts that grow on trees. The peanut plant flowers above ground but the peanut pods develop below the soil.
What Type Of Climate Do Peanuts Need To Grow?
Peanuts thrive in warm climates with well-drained soil and plenty of sunshine. They require about 4-5 months of frost-free growing days to reach maturity.
What Is The Growing Process Of Peanuts?
Peanuts are planted in early to mid-spring and take 4-5 months to reach maturity. The plants flower and then develop pegs, which enter the soil and form the peanut pods.
How Do Farmers Harvest Peanuts?
Farmers typically harvest peanuts using specialized equipment that lifts the plants and shakes the excess soil from the roots. After drying, the peanuts are then picked off the plant for further processing.
Conclusion
Peanuts are a fascinating crop that can grow in a variety of climates and soils. With their unique underground fruiting habit and high nutritional value, they are an important food source for people and animals alike. From planting to harvest, understanding the growth process of peanuts can help farmers optimize their yields and provide consumers with high-quality products.
By following the right techniques and ensuring proper care, anyone can grow peanuts in their own backyard and enjoy the delicious taste of fresh, homegrown nuts.